Understanding the thyroid: all you need to know
The thyroid is a butterfly-shaped gland in the neck that plays a crucial role in regulating many bodily functions, including metabolism, growth and development. This comprehensive guide will inform you of everything you need to know about the thyroid gland, including how it works, the health problems it can cause and the treatments available.
WHAT IS THE THYROID GLAND AND HOW DOES IT WORK?
The thyroid is an endocrine gland that produces thyroid hormones, which regulate metabolism and growth. It works by absorbing iodine from food and using it to make the thyroid hormones T3 and T4.
These hormones are then released into the blood and transported to the body’s cells, where they regulate metabolism and growth. It is also regulated by the pituitary gland, a gland in the brain that produces thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) to control the production of thyroid hormones.
If the thyroid gland does not produce enough hormones or releases too many, you may develop a thyroid disorder. Some people have mild hypothyroidism (low production) or hyperthyroidism (high production). Others have more serious conditions, such as Graves’ disease or Hashimoto’s disease, which can lead to complications if left untreated.
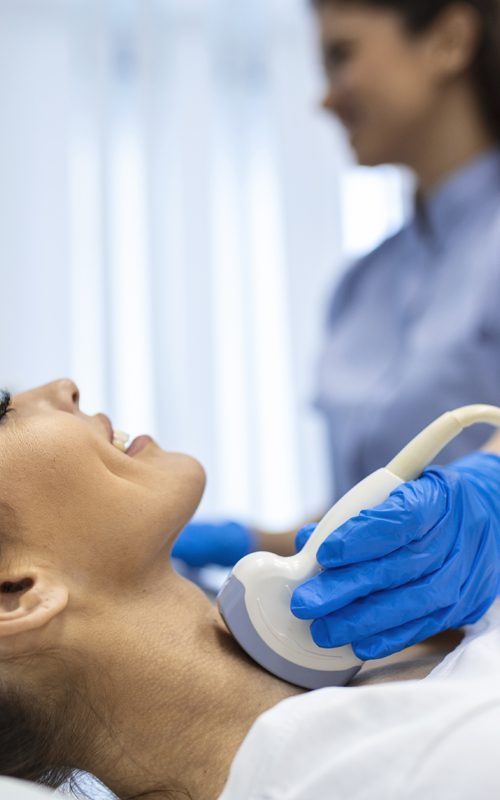
DIFFERENT TYPES OF THYROID DISEASE
There are several types of thyroid disease, including hypothyroidism, hyperthyroidism, thyroiditis and thyroid nodules.
Hypothyroidism occurs when the thyroid gland does not produce enough thyroid hormone, which can lead to weight gain, tiredness, constipation and dry skin.
Hyperthyroidism occurs when the thyroid gland produces too much thyroid hormone, which can cause weight loss, nervousness, heart palpitations and excessive sweating.
Thyroiditis is an inflammation of the thyroid gland, which can cause pain and swelling.
Thyroid nodules are masses that form in the thyroid gland and it can be benign or malignant. Thyroid nodules are common and may be asymptomatic unless they are large enough to put pressure on surrounding structures. Large nodules are more likely than small ones to cause symptoms such as difficulty swallowing or breathing.
WHAT IS CONVENTIONAL THYROID SURGERY?
Conventional thyroid surgery is performed through an incision in the front of the neck. The surgeon will perform a partial or total thyroidectomy, depending on the patient’s condition.
Partial thyroidectomy:
In a partial thyroidectomy, only part of the gland is removed, leaving the parathyroid glands intact. This type of surgery is used when there are benign nodules or when there are no nodules but there is a risk of cancer developing. It can also be done if a severe goiter is blocking the airways. It can be performed on an outpatient basis and requires a short stay in hospital.
Total thyroidectomy:
Total thyroidectomy involves the removal of the entire thyroid gland and adjacent lymph nodes, but it does not include removal of the parathyroid glands. Total thyroidectomy can be performed for cancer and is an outpatient procedure with minimal recovery time. The result is hypothyroidism (underactive thyroid).
WHAT'S A GOITER?
A goiter is an enlargement of the thyroid gland. It can be caused by iodine deficiency, lack of thyroid hormone, or abnormal thyroid function.
Iodine deficiency is the most common cause of goiter worldwide. It can occur in people who do not get enough iodine in their diet, or who have a reduced ability to absorb and use iodine, even if they eat foods that contain adequate amounts of the mineral.
In addition to a lack of iodine in the diet, some drugs interfere with the absorption or use of iodine, leading to the condition. These include certain antibiotics (such as ampicillin), anti-epileptic drugs (such as phenytoin), thiazide diuretics (such as hydrochlorothiazide), potassium supplements, and lithium therapy for bipolar disorder.
Goiter can also be caused by abnormal thyroid function. This can be caused by the thyroid gland producing too much thyroid hormone, or the pituitary gland, a pea-sized gland located at the base of the brain, behind the nose and eyes, producing too little thyroid hormone.
If you do not get enough iodine, you may feel tired, weak and gain weight. You may feel cold because your body has trouble maintaining its normal temperature if it does not get enough iodine.
THE SYMPTOMS
Thyroid symptoms vary depending on the type of thyroid problem and its course or treatment. Symptoms may include:
– Restlessness, nervousness, emotionality, irritability, sleep problems and hyperactivity.
– hands tremors.
– Weight loss despite a fairly large appetite.
– Heart palpitations.
– Sweating, heat intolerance and increased thirst.
– Diarrhoea or more frequent bowel movements than normal.
– Difficulty breathing.
– Skin problems like hair loss and itching.
– Changes in menstrual cycle.
– Tiredness and muscle weakness.
– Increased size of the thyroid gland (goiter).
THE CAUSES OF THYROID DISORDERS
Thyroid disorders can cause a variety of symptoms, including weight gain or loss, tiredness, sleep problems, mood changes, skin problems, and digestive problems. The causes of thyroid disorders can vary, but may include genetic factors, infections, autoimmune diseases and nutritional deficiencies. It is important to see a doctor if you have symptoms of a thyroid condition to get an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment.
DIAGNOSTIC TESTS AND TREATMENTS
If you have symptoms of thyroid disease, your doctor may prescribe diagnostic tests such as blood tests to measure thyroid hormone levels or ultrasound scans to examine the thyroid gland. Treatment for thyroid disorders depends on the underlying cause and may include medication to regulate thyroid hormone levels, surgery to remove the thyroid gland, or treatment with radioactive iodine to destroy thyroid cells. It is important to discuss the treatment options available for your specific case with your doctor.

TIPS FOR MAINTAINING A HEALTHY THYROID
There are several ways to keep your thyroid gland healthy. Firstly, it is important to get enough iodine, an essential mineral for the production of thyroid hormones. Foods rich in iodine include seafood, iodised salt and dairy products. It is also important to eat a balanced diet and take regular exercises to maintain a healthy weight. You should also avoid smoking and excessive alcohol consumption, as these can affect thyroid function. Finally, see your doctor regularly to monitor your thyroid health.

