Paediatric surgery deals with the surgical treatment of children from the foetal period to adolescence.
PAEDIATRIC VISCERAL SURGERY
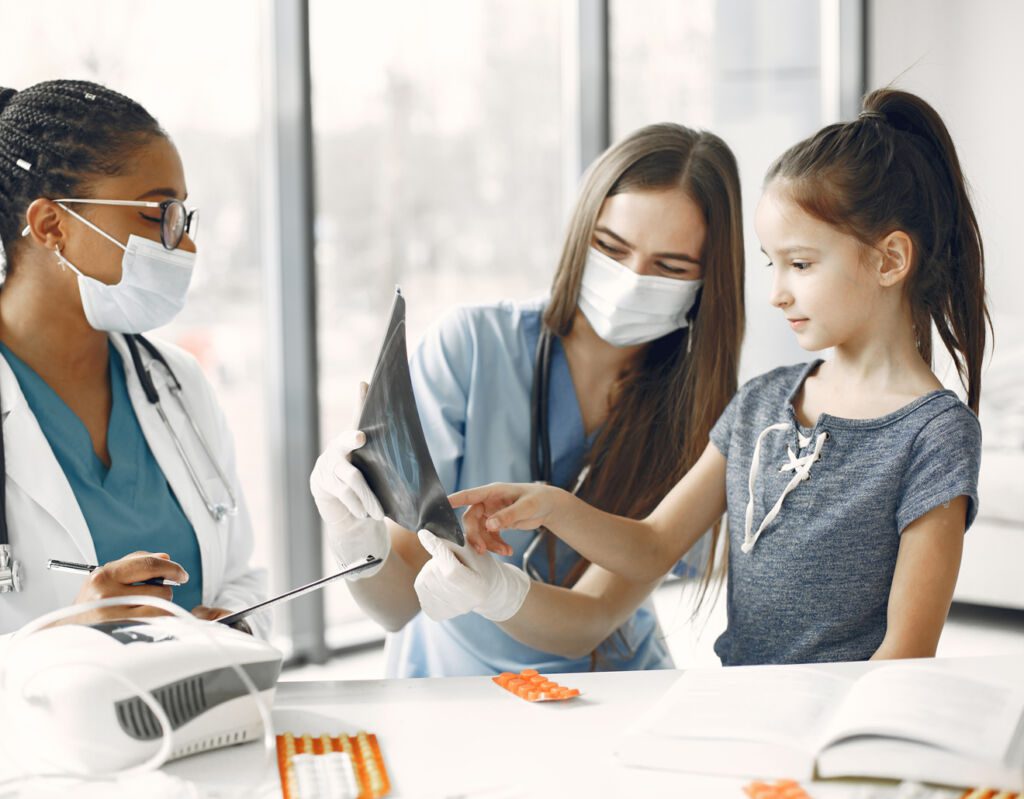
Paediatric visceral surgery is a surgical subspeciality that focuses on the treatment of conditions affecting the major organ systems of children.
This may include the treatment of cancer, congenital heart disease and chronic liver failure. Visceral surgery encompasses a wide range of procedures including but not limited to gastrointestinal, hepatobiliary and pancreatic, thoracic, cardiovascular and neurosurgery.

PAEDIATRIC ORTHOPAEDIC SURGERY
Paediatric orthopaedic surgery, also known as paediatric orthopaedics, is a speciality of orthopaedics that focuses on the treatment of musculoskeletal injuries in children.
It deals with both the surgical and non-surgical aspects of diseases, deformities and trauma affecting the bones, joints and muscles of children.
Paediatric orthopaedic surgeons must have a thorough knowledge of the musculoskeletal system of children at all stages of development, from birth to adolescence. They often work closely with other paediatric specialists, such as paediatricians, geneticists and psychologists, to provide comprehensive care for patients with complex medical needs.
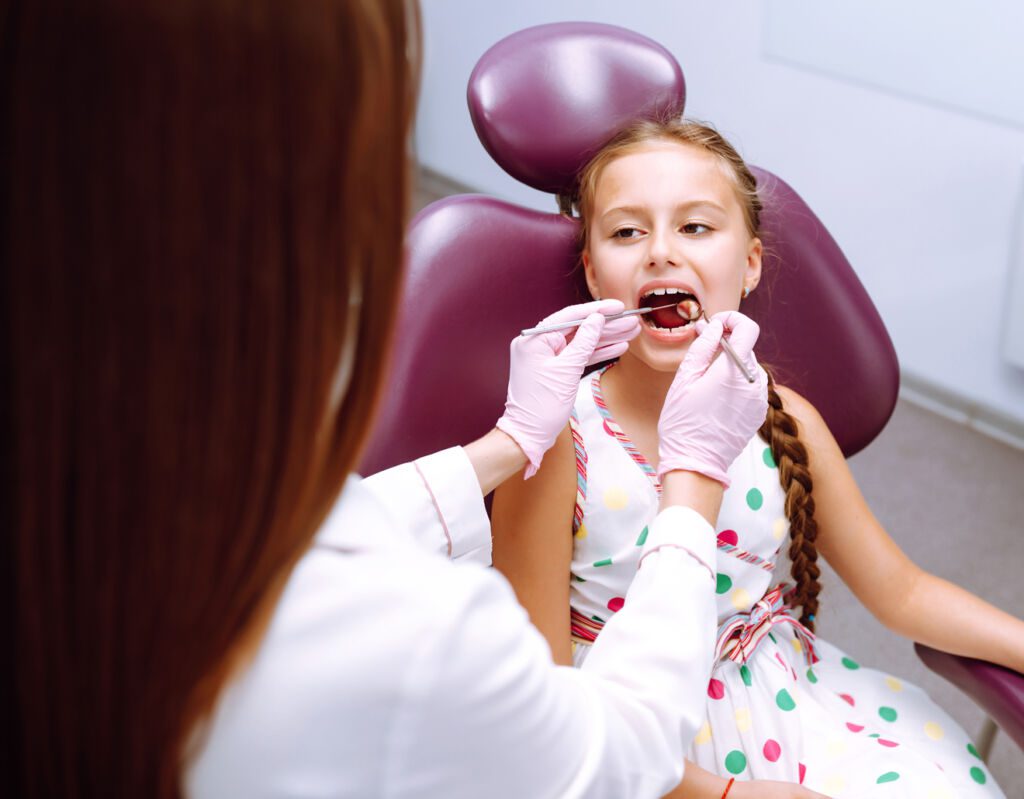
PAEDIATRIC DENTAL SURGERY
Paediatric dental surgery is the use of surgery to treat diseases and injuries of the mouth, teeth, gums and jaws of newborn babies.
It is usually performed by a paediatric dentist or an oral and maxillofacial surgeon.
Paediatric dental procedures include:
- Extractions – removal of teeth
- Wisdom tooth extraction – removal of the wisdom teeth in the back of the mouth, behind the last molars.
- Root canal treatment – treating an infection in the pulp chamber of a tooth by cleaning out the infected tissue and filling the root canal with a material that prevents bacteria from re-entering the canal.
- Malocclusion or crooked teeth (orthodontics) – moving teeth into a better position by attaching braces to one or more dental arches.
PAEDIATRIC PLASTIC SURGERY
Paediatric Plastic Surgery is a specialised form of surgery that treats the plastic surgery problems of children and adolescents. This specialty includes the treatment of congenital anomalies and acquired defects that affect growth, development and appearance.
Paediatric plastic surgeons specialise in the diagnosis and treatment of children with congenital deformities, facial deformities, disfigurement and trauma. Paediatric plastic surgeons also perform reconstructive surgery on children who have suffered burns or whose faces have been disfigured by disease.
Paediatric plastic surgery is the surgical specialty that treats abnormalities of the face, ears, nose and neck in children. These abnormalities can be congenital or acquired and include cleft lip, cleft palate and skin abnormalities such as haemangiomas.
You ask, our teams answer.
F.A.Q
Paediatric surgery is a branch of surgery that deals with the surgical care of infants, children and adolescents. Paediatricians and surgeons who specialise in paediatric surgery are called paediatric surgeons.
Paediatric surgeons are often involved in the care of newborn babies with congenital anomalies and the treatment of children with cancer or other complex conditions. They may also perform corrective surgery on children with congenital deformities or injuries.
There are three types of paediatric surgery:
- General surgery: general surgeons receive additional training in paediatric surgery to treat children up to the age of 19.
- Neonatal and perinatal medicine: Specialists in neonatal and perinatal medicine receive advanced training to care for newborn babies who have suffered complications during pregnancy or childbirth, as well as premature babies who require special care after birth.
- Paediatric intensive care medicine: Specialists in paediatric intensive care receive advanced training to ensure the life support of critically ill infants, children and adolescents with complex problems requiring long-term intensive care.
Orthodontics is a branch of dentistry concerned with the prevention, diagnosis and treatment of malocclusion or abnormal positioning of the teeth and related oral structures. Orthodontics is concerned with the development and growth of the jaws and facial bones and their relationship to each other. Orthodontics also includes the study, diagnosis, prevention and treatment of malocclusion.
Orthodontics uses a variety of treatments to align teeth when they do not meet the requirements of normal function. The most common orthodontic treatment is the use of braces to move teeth into position. Orthodontic treatment can be used to correct problems such as missing teeth, crowding, underbite, overbite, space between teeth (diastema), open bite (gap) or crossbite (teeth not aligned).
Paediatric orthopaedics is a subspeciality of paediatrics. It deals with the musculoskeletal problems of infants, children and adolescents. It includes all pathologies affecting the musculoskeletal system from birth to adolescence. Conditions treated include congenital anomalies such as clubfoot or hip dislocation, fractures, injuries such as sports injuries, degenerative joint diseases such as osteoarthritis, spondylolisthesis, scoliosis, malformations such as cerebral palsy or Down’s syndrome, tumours such as osteoid osteoma, infections such as osteomyelitis.

