
Volvulus, a frequently underestimated medical emergency, deserves your full attention. It occurs when the intestine twists on itself, causing a blockage that can quickly become critical. Recognizing the symptoms at the first sign can be vital: intense abdominal pain, vomiting, and bloating can indicate intestinal distress. In this article, we will guide you through the causes and consequences of this concerning condition, while also exploring available treatments and preventive measures to adopt. By understanding volvulus, you will be better equipped to act quickly when needed and protect your health and that of your loved ones. Let’s dive into this essential topic together to better understand an emergency that could save lives.
What is volvulus?
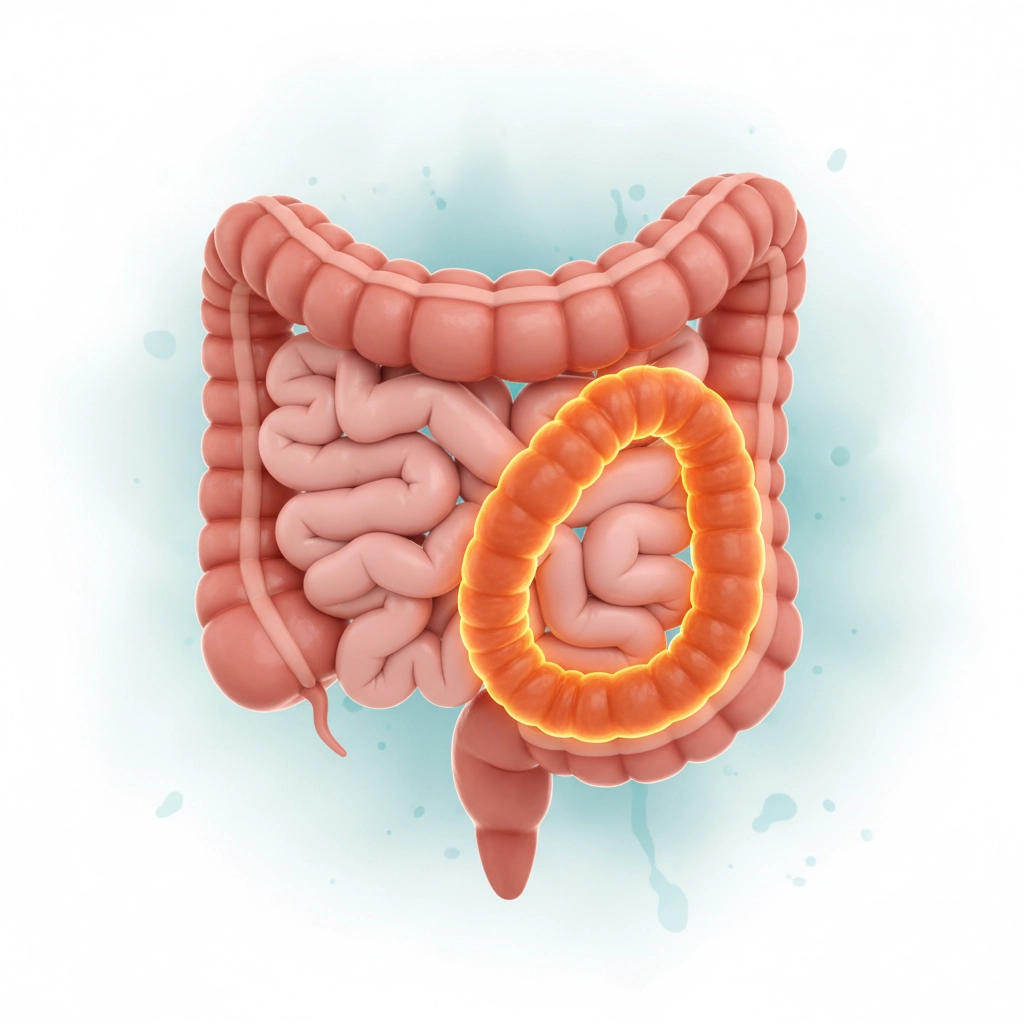
A volvulus is a serious medical condition characterized by the twisting of the intestine on itself. This twisting causes an obstruction, preventing intestinal contents from passing through normally. This phenomenon can occur at different levels of the digestive tract, most often in the small intestine or colon. The seriousness of the situation lies in the fact that this twisting can cut off the blood supply to the affected part of the intestine, leading to tissue necrosis if not treated quickly.
The frequency of this condition varies with age and certain risk factors. Infants, especially those with congenital intestinal malformations, are more likely to develop a volvulus. In adults, this condition can occur as a result of certain chronic diseases or previous surgical interventions. It is crucial to understand that a volvulus is a medical emergency requiring rapid intervention to avoid serious, or even fatal, complications.
Early diagnosis and treatment of a volvulus are essential to reduce the risk of complications. Recognizing the symptoms and understanding the potential causes can lead to swift and effective intervention. By learning about this condition, one can be better prepared to act on alarming symptoms, which can mean the difference between a quick recovery and devastating consequences.
Causes and Risk Factors of Volvulus
The causes of a volvulus can vary considerably from one person to another. In infants, the main cause is often a congenital intestinal malrotation, a condition where the intestines do not form correctly in the womb. This malformation can lead to a twisting of the intestine, especially in the first few months of life. Adults, on the other hand, can develop a volvulus due to factors such as post-operative adhesions, hernias, or even certain inflammatory bowel diseases.
Risk factors also include conditions such as short bowel syndrome, where a part of the intestine has been removed, thus increasing the likelihood of twisting. Patients who have undergone major abdominal surgery are also at risk, as scars and adhesions can promote the twisting of the intestines. Additionally, certain dietary habits and lifestyles can contribute to the development of a volvulus, particularly a high-fiber diet that is not well-chewed and insufficient hydration.
It is also important to note that certain anatomical abnormalities can predispose a person to a volvulus. For example, an abnormally long mesentery or insufficient fixation of the intestines can facilitate their twisting. Knowing these risk factors and discussing them with a healthcare professional can help in implementing preventive strategies to minimize the risks of developing this potentially life-threatening condition.
Common Symptoms of Volvulus
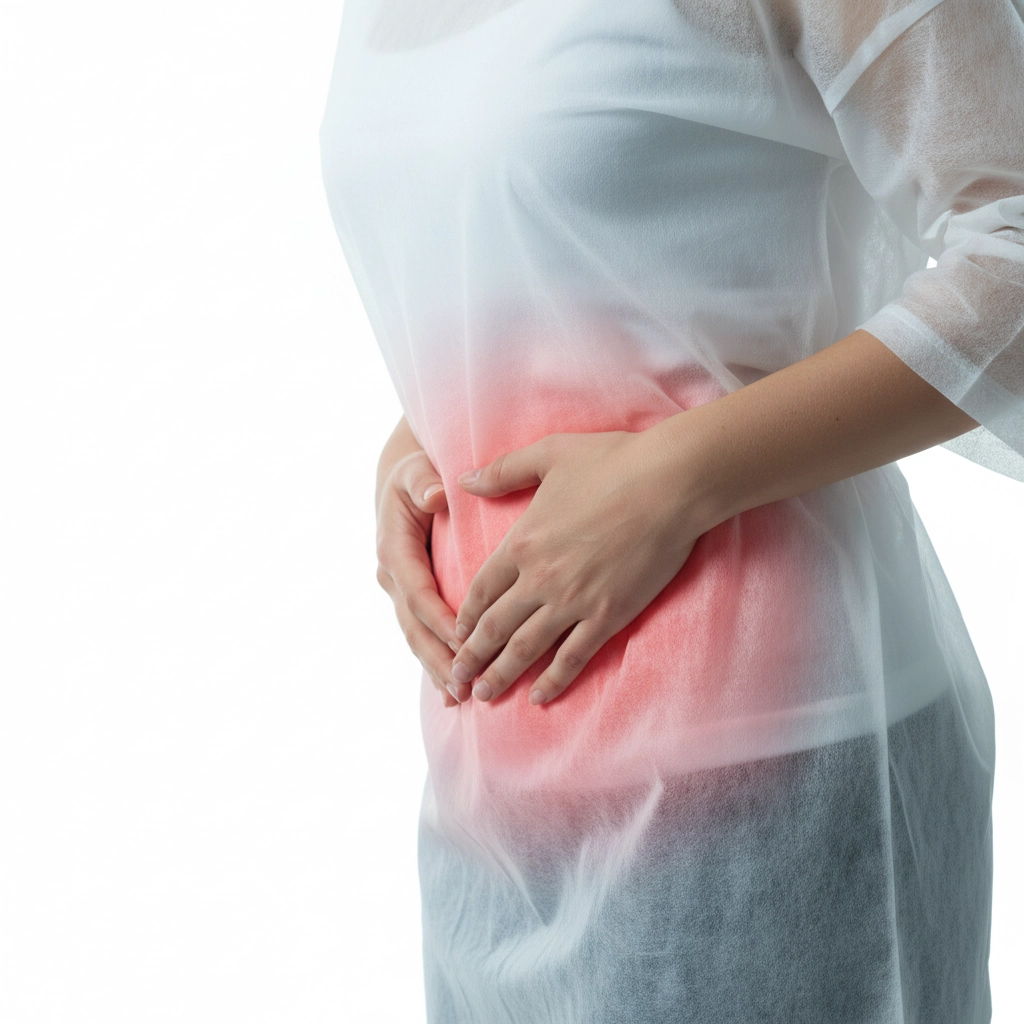
The symptoms of volvulus can appear quickly and intensely. One of the first signs is severe, sudden abdominal pain, often described as a cramp or spasm. This pain can be localized or widespread and is often accompanied by nausea and vomiting. The vomit may be bilious, meaning it contains bile, which is particularly common when the volvulus affects the small intestine.
In addition to pain and vomiting, patients may also experience significant abdominal bloating. This bloating is due to the accumulation of gas and fluids in the blocked intestine. Constipation is another common symptom, as the blockage prevents the normal passage of stool. In some cases, patients may show signs of shock, such as a rapid heart rate, low blood pressure, and excessive sweating, indicating severe systemic distress.
It is crucial not to ignore these symptoms, as prompt diagnosis and treatment are essential to avoid serious complications. If you or a loved one experience these signs, it is imperative to seek immediate medical attention. Quick recognition of symptoms can lead to rapid medical intervention, thereby reducing the risk of intestinal necrosis and other potentially fatal complications.
Diagnosing volvulus
The diagnosis of volvulus is based on a combination of clinical evaluations and medical imaging tests. During the physical exam, the doctor will look for signs of acute abdominal pain, bloating, and tenderness. A detailed medical history is also crucial to identify risk factors and past medical issues that could contribute to the condition. However, a clinical exam alone is not enough to confirm the diagnosis.
Imaging tests play a key role in diagnosing volvulus. An abdominal X-ray can show classic signs of obstruction, such as air-fluid levels and dilated intestinal loops. However, the preferred test is often a computed tomography (CT) scan, which can provide detailed images of the twisted intestine and the extent of the obstruction. The CT scan also helps assess the blood supply to the intestine, which is critical for determining the urgency of the intervention.
In some cases, other tests like magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) or an endoscopy may be necessary to further evaluate the structure and function of the intestine. Once the diagnosis is confirmed, it is essential to begin treatment immediately to avoid serious complications such as tissue necrosis, intestinal perforation, and peritonitis. A quick and accurate diagnostic approach is therefore essential for the effective management of volvulus.
Potential complications of volvulus
Volvulus is a condition that can lead to serious and potentially life-threatening complications if not treated quickly. One of the most feared complications is intestinal necrosis. When the intestine is twisted, the blood supply is compromised, which can lead to the death of intestinal tissue. This necrosis can lead to intestinal perforation, releasing the contents of the intestine into the abdominal cavity and causing peritonitis, a serious infection of the abdomen.
Another potential complication is septic shock. Peritonitis or intestinal necrosis can cause a severe systemic infection, leading to a widespread inflammatory response. This septic shock can cause multiple organ failure, affecting vital organs like the heart, kidneys, and lungs. Without rapid medical intervention, septic shock can be fatal. Patients must be closely monitored for any signs of rapid deterioration.
Finally, even after successful treatment, some people may experience long-term complications. These can include adhesions that may cause recurrent intestinal obstructions, reduced intestinal motility, and chronic digestive problems. Prompt recognition and management of complications are essential to improve long-term outcomes and the quality of life for patients.
Treatment options for volvulus
The treatment for volvulus depends on the severity of the symptoms and the extent of the intestinal obstruction. In less severe cases, an endoscopic decompression may be attempted. This procedure involves inserting an endoscope into the intestine to try to untwist it and relieve the obstruction. However, this method is not always effective and is generally reserved for cases where surgery is not immediately necessary.
The majority of volvulus cases require surgery. The goal of surgery is to untwist the intestine and restore normal blood flow. In cases where the intestine shows signs of necrosis (tissue death), the affected part must be removed to prevent infection and further complications. This procedure is known as an intestinal resection. After the resection, the healthy ends of the intestine are reconnected in a procedure called anastomosis.
In some cases, a temporary or permanent stoma may be necessary if an extensive resection is performed or if anastomosis is not possible immediately. A stoma is an artificial opening created on the abdomen to allow stool to exit the body. It is crucial to discuss treatment options with a healthcare professional to understand the risks and benefits of each approach and make an informed decision.
Surgery: When is it necessary?
Surgery is often necessary to treat volvulus, especially when the condition is accompanied by severe symptoms or complications. Surgical indications include intense abdominal pain, signs of intestinal necrosis, perforation, and signs of peritonitis. In these situations, prompt treatment is essential to avoid life-threatening complications. Surgery is also indicated when non-invasive methods, such as endoscopic decompression, fail to resolve the obstruction.
During surgery, the surgeon aims to untwist the intestine and assess the viability of the tissue. If a part of the intestine is necrotic, it must be removed to prevent infection and peritonitis. This procedure, although invasive, is often the only option to save the patient’s life. Surgical techniques can vary, ranging from open laparotomy to laparoscopy, a less invasive method that uses small incisions and specialized instruments.
It is essential to understand that surgery for volvulus is not without risks. Possible complications include infections, bleeding, and the formation of adhesions that can lead to future obstructions. However, the benefits of surgery generally outweigh the risks, especially in cases of acute volvulus. Consultation with an experienced surgeon and a competent medical team is crucial for optimal management.
Preventing Volvulus

Preventing a volvulus may not always be possible, especially in cases of congenital malformations or predisposing anatomical factors. However, certain measures can be taken to reduce the risk of developing this condition. A balanced, high-fiber diet can help maintain regular bowel movements, thus reducing the risk of intestinal twisting. It is also important to stay adequately hydrated to promote healthy digestion.
Managing underlying medical conditions is also crucial. People with inflammatory bowel disease, diverticulitis, or other gastrointestinal disorders should follow their doctor’s recommendations to minimize risks. Patients who have had abdominal surgery should be aware of the signs and symptoms of adhesions and consult their doctor for recurrent abdominal pain or changes in bowel habits.
Finally, education and awareness are key elements of prevention. Understanding the symptoms of a volvulus and knowing when to see a healthcare professional can make a significant difference. Parents of at-risk infants should be particularly vigilant and seek immediate medical care if alarming symptoms appear. Prevention, therefore, involves a combination of dietary strategies, management of underlying conditions, and education.
Recovery After Volvulus Treatment
Recovery after volvulus treatment depends on the initial severity of the condition and the type of treatment received. Patients who have undergone surgery generally require a longer recovery period. After surgery, it is essential to monitor for signs of infection, follow a suitable diet, and attend regular follow-up appointments. Postoperative care often includes pain management, monitoring of bowel function, and preventing complications.
Patients can also benefit from the help of a nutritionist to adjust their diet during the recovery period. A balanced diet and frequent but light meals can help restore bowel function and prevent complications. Fiber should be introduced gradually to avoid irritating the recently operated intestines. Additionally, adequate hydration is crucial for promoting healing and proper bowel function.
Psychological support should not be overlooked, as recovering from a volvulus can be a trying experience. Patients may experience anxiety or depression related to their medical condition. Support groups or therapy sessions can be beneficial for coping with the emotional aspects of recovery. Ultimately, a holistic approach that includes medical, nutritional, and psychological care is essential for a complete and successful recovery.
Conclusion and Advice for Patients

Volvulus is a serious medical emergency that requires immediate attention. Recognizing the symptoms and understanding the causes and risk factors are key to early and effective intervention. Treatment options vary depending on the severity of the condition, ranging from endoscopic decompression to emergency surgery. Prevention and recovery involve careful management of intestinal health, a balanced diet, and regular medical follow-ups.
For patients and their loved ones, it is crucial to know the warning signs of volvulus and not hesitate to consult a healthcare professional if there is any doubt. Prompt care can make the difference between a quick recovery and serious complications. Additionally, following post-treatment recommendations and adopting a healthy lifestyle are essential steps to prevent recurrence and ensure good intestinal health.
Finally, it is important to remember that every patient is unique, and treatment plans should be personalized to meet individual needs. Collaboration with healthcare professionals, continuous education, and emotional support are key elements in effectively managing this condition. By gaining a better understanding of volvulus and taking proactive measures, patients can improve their chances of recovery and lead a healthy, balanced life.

